Operations Management- From Strategy to Execution
In today’s fast-moving and highly competitive business world, operations management plays a decisive role in determining how well an organization performs.
In simple terms, it is the discipline that plans, organizes, and controls how a company converts resources such as people, materials, and technology into valuable products and services. It ensures that process management across departments works smoothly so that business and operations stay aligned with customer demand and market expectations.
As global and Indian companies face rising costs, labor shortages, supply chain disruptions, and increasing customer expectations, the importance of operations management has never been greater. Inefficient operations, poor quality control, or delayed deliveries can directly impact profitability and brand reputation. Whether in service or manufacturing operations, strong management helps organizations achieve their objectives of—higher productivity, consistent quality, and reliable delivery.

Modern businesses can no longer view operations as a back-office or factory-floor function. Today, a well-defined operations strategy is central to achieving scalability, cost leadership, and customer satisfaction. By optimizing the functions, organizations can overcome key challenges such as waste, bottlenecks, and variability. This growing relevance of operations management makes it a powerful strategic tool for building competitive advantage and long-term business success.
What Is Operations Management?
It refers to the systematic planning, control, and improvement of all activities that transform resources into finished goods and services. At its core, operations management ensures that it deliver maximum value to customers while using time, money, and materials efficiently. Through effective processes management, organizations align their operations so that every function—from procurement to delivery—works toward common performance goals.
Unlike production management, which focuses mainly on making products on the factory floor, business operations management covers a much broader scope. It includes planning capacity, managing inventory, maintaining quality, designing workflows, and building an effective strategy. While production is one part of the system, the functions of operations management ensure that the entire value chain works smoothly.
The importance of operations management lies in how well it converts inputs such as labor, capital, energy, and raw materials into reliable outputs that meet customer expectations. Its objectives include cost control, quality consistency, speed, and flexibility. In today’s complex business environment, the growing relevance of operations management is driven by rising customer demands and increasing challenges, making strong operational control essential for sustainable growth.
Core Objectives of Operations Management
The objectives of operations management define how effectively an organization designs and controls its operations to achieve business success. In both services and manufacturing operations, these objectives guide how resources are used to create consistent value for customers.
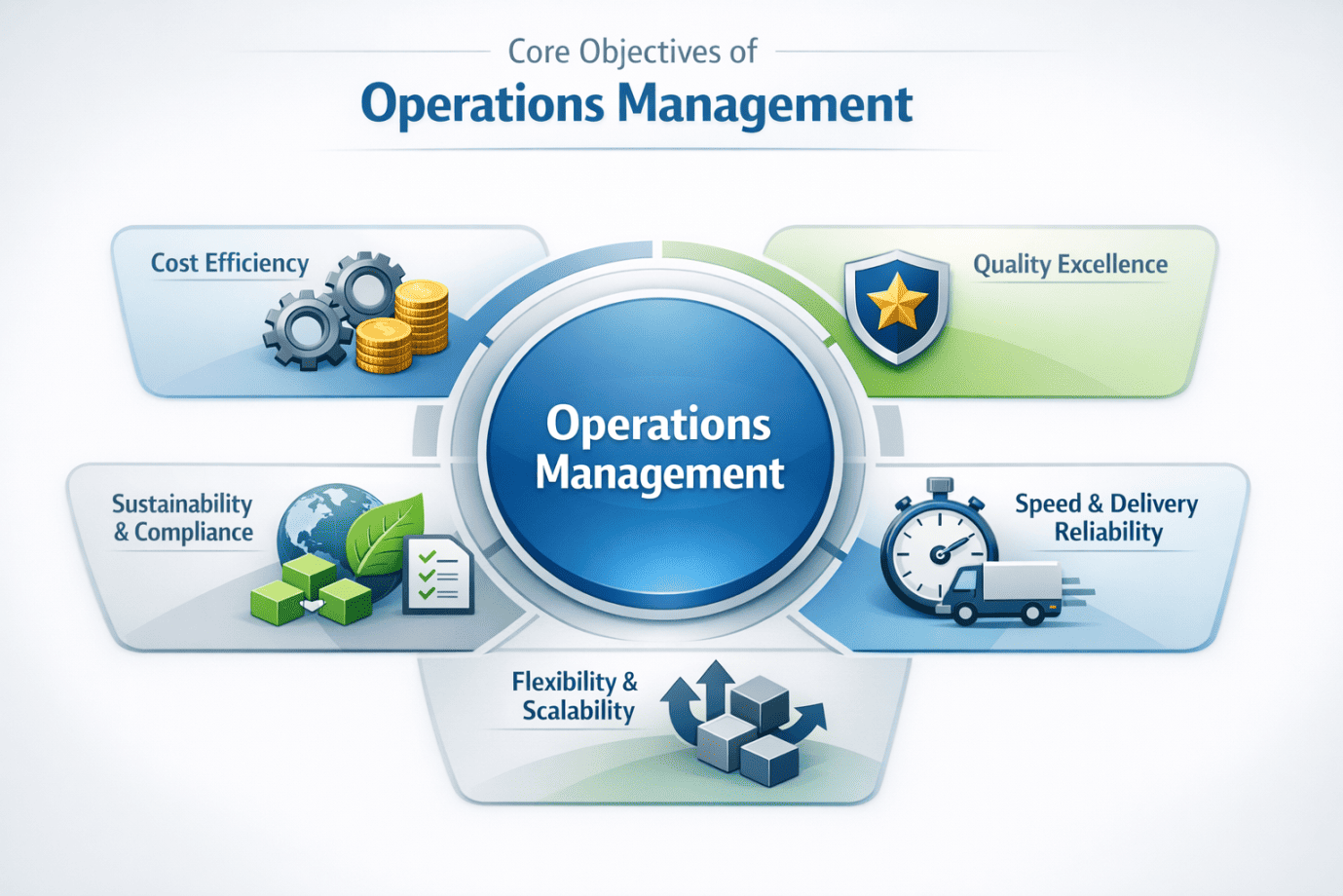
- Cost Efficiency: One of the primary goals is to minimize waste and improve productivity through effective process management. By streamlining workflows, reducing idle time, and improving material usage, organizations can lower costs while strengthening their business and operations
- Quality Excellence: Another critical element is ensuring high and consistent quality. Well-defined functions help reduce defects, improve reliability, and increase customer satisfaction, reinforcing the importance of operations management in building brand trust.
- Speed & Delivery Reliability: A strong operations strategy focuses on shortening lead times and ensuring on-time delivery. Faster, predictable output helps companies overcome key challenges such as backlogs and customer dissatisfaction.
- Flexibility & Scalability: The growing relevance of operations management is seen in its ability to help organizations respond to demand fluctuations without disrupting company operations or profitability.
- Sustainability & Compliance: Modern operations management also integrates safety, ESG standards, and regulatory compliance into everyday decision-making, ensuring responsible and future-ready business performance.
Key Functions of Operations Management
The functions of operations management form the backbone of how organizations design, control, and improve their operations. Whether in services or manufacturing operations, these functions ensure that business and operations remain aligned with customer expectations and financial goals.
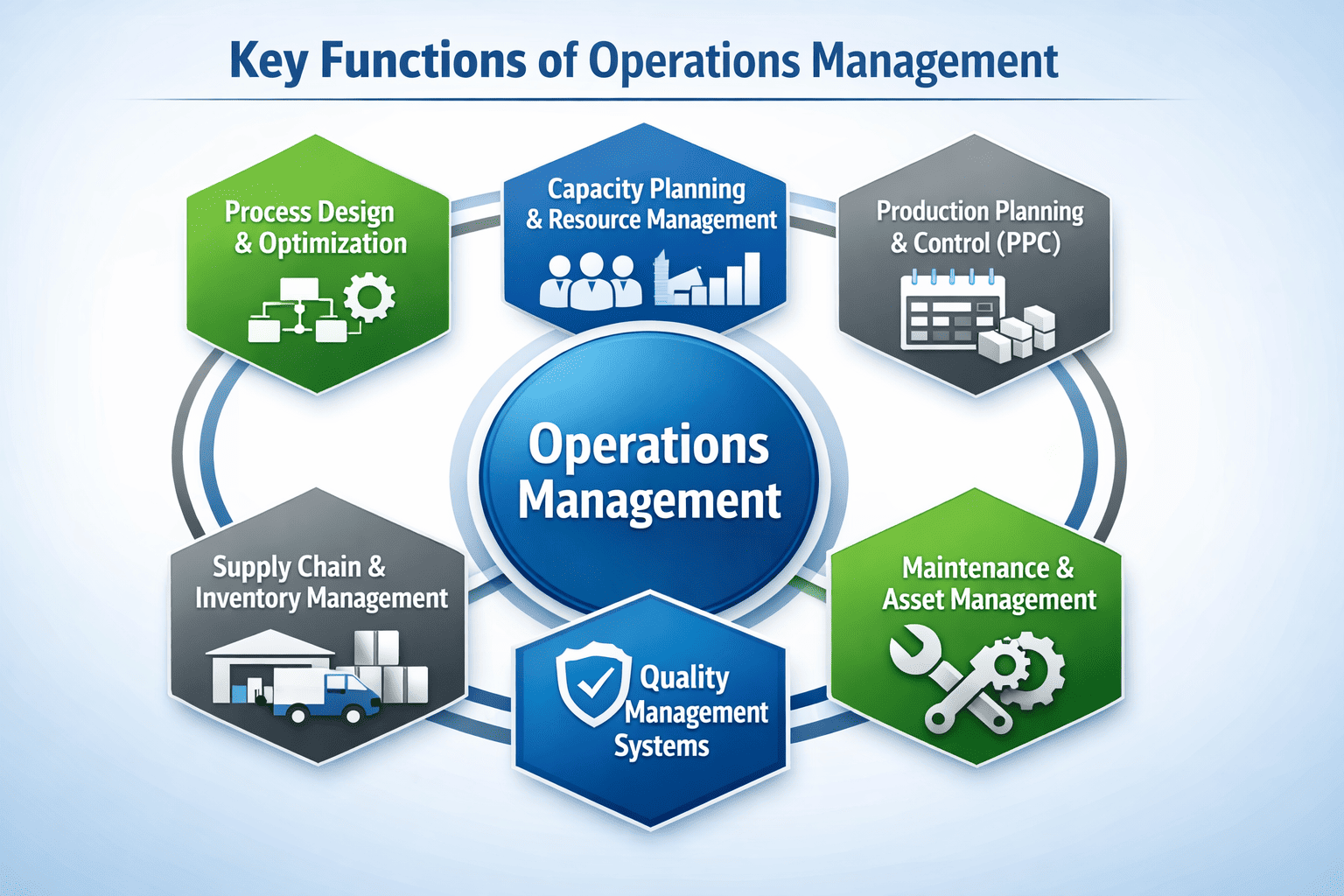
Process Design & Optimization
A core responsibility of operations management is building efficient workflows through effective process management. This includes mapping activities, removing bottlenecks, and eliminating waste to ensure that inputs are converted into outputs with minimal effort and cost. Well-optimized processes directly support the objectives such as productivity, quality, and speed.
Capacity Planning & Resource Management
Through strategic planning, business operations management determines how much labor, equipment, and space is needed to meet demand. A well-designed strategy ensures that resources are neither underutilized nor overstretched, helping organizations overcome major challenges like excess inventory or delayed deliveries.
Production Planning & Control (PPC)
In manufacturing operations, PPC ensures that materials, machines, and people are synchronized. This function balances workloads, controls work-in-progress, and ensures that output meets customer requirements on time.
Supply Chain & Inventory Management
A key element of modern operations management is managing supplier networks and stock levels. Strong coordination across the supply chain reduces shortages, improves cash flow, and strengthens overall operations.
Quality Management Systems
Quality is central to the operations management. Structured systems ensure that products and services meet defined standards, reducing defects and improving customer trust.
Maintenance & Asset Management
Maintaining equipment reliability protects production flow and supports the growing relevance of operations management in sustaining long-term performance across both manufacturing and services operations.
Together, these interconnected functions allow organizations to execute their strategy effectively and achieve lasting operational excellence.
Operations Management in Manufacturing vs Services
While operations management applies to every industry, its execution differs significantly between manufacturing and services operations. The way process is designed depends on the nature of work, customer involvement, and output variability. In manufacturing, workflows are typically structured, equipment-driven, and highly dependent on material flow, whereas in services, activities are more people-centric and influenced by customer interaction.
- In manufacturing operations, the primary focus is on productivity, machine uptime, inventory control, and minimizing downtime. Even small inefficiencies can create major challenges such as production delays, excess scrap, and high operating costs. Here, a strong strategy relies heavily on engineering analysis, capacity planning, and data-driven process optimization to achieve the objectives.
- In contrast, services operations prioritize responsiveness, customer experience, and capacity utilization. The performance of company operations in service industries is closely linked to how well employees interact with customers and how quickly requests are fulfilled. While efficiency is still important, flexibility and service quality define the importance of operations management in this context.
The growing relevance of operations management is most evident in manufacturing, where deeper engineering, automation, and analytics are required to balance cost, quality, and speed. By aligning business and operations, organizations in both sectors can build reliable, scalable, and competitive operational systems.
Common Operations Management Challenges Faced by Businesses
Businesses operating in today’s highly competitive environment face numerous challenges that affect productivity, cost control, and customer satisfaction. Whether in manufacturing or services, weak operations can prevent organizations from achieving the true importance.
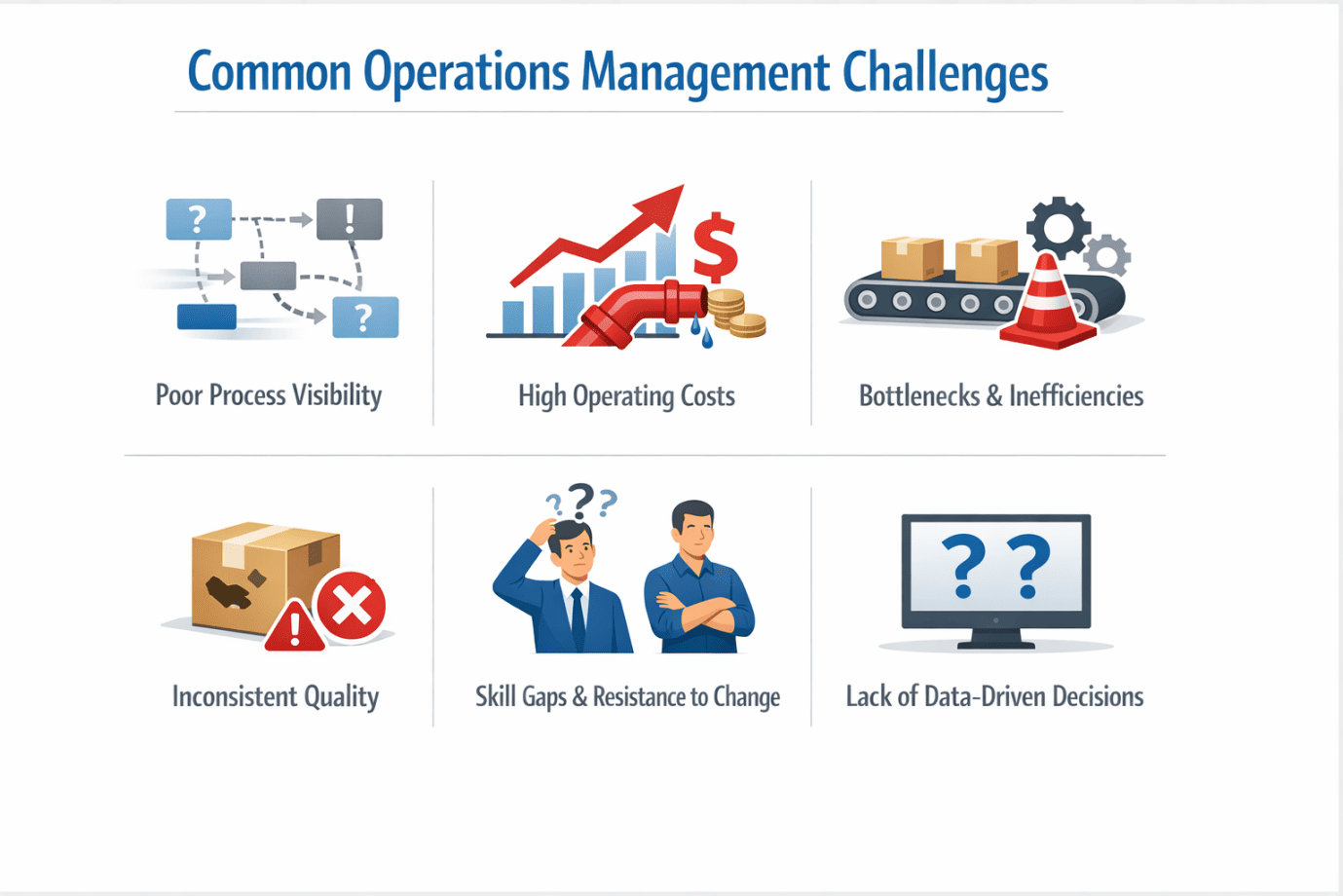
Poor Process Visibility
One of the biggest problems is the lack of visibility across workflows. Without structured processes management, organizations struggle to identify where delays, waste, or errors occur. In many Indian MSMEs, rapid business growth leads to disconnected operations, making it difficult to control performance or improve efficiency
High Operating Costs
Inefficient use of labor, materials, and equipment leads to rising costs. When resources are not planned properly, organizations fail to meet their objectives, reducing profitability and competitiveness—especially in cost-sensitive manufacturing operations.
Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies
Bottlenecks disrupt the smooth flow of work and create delays in company operations. Weak functions such as poor line balancing and ineffective scheduling result in idle time, excess inventory, and late deliveries.
Inconsistent Quality
Without standardized processes, quality varies. This weakens the importance, as defects, rework, and customer complaints increase across both manufacturing and services operations.
Skill Gaps and Resistance to Change
Many organizations lack trained personnel to execute a modern strategy. Resistance to change further limits the relevance of operations management, preventing the adoption of better systems and practices.
Lack of Data-Driven Decision Making
Without real-time data, operations management becomes reactive rather than strategic. Strong management depends on analytics to improve performance and overcome operational risks.
Modern Tools & Techniques in Operations Management
In today’s dynamic business environment, successful operations management depends on the intelligent use of modern tools that continuously improve company operations. These tools are not one-time fixes but long-term enablers that support strong process management, adaptability, and sustainable performance across manufacturing and services operations.
Lean Manufacturing & Waste Reduction
Lean principles help eliminate non-value-adding activities from business operations management. By identifying and removing waste, organizations improve efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve the objectives such as higher productivity and faster delivery.
Industrial Engineering Tools
Techniques like time and motion studies, line balancing, and Value Stream Mapping (VSM) strengthen the functions by providing clear insight into how work flows through a system. These tools help detect bottlenecks, optimize labor usage, and overcome key challenges in complex manufacturing operations. For detailed information, you can go through our dedicated blog on Value Stream Mapping.
Six Sigma & Continuous Improvement
Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation and defects. By using structured problem-solving methods, organizations align business and operations with customer expectations, reinforcing the importance of operations management in delivering consistent quality. For more information, you can read our detailed blog on Six Sigma.
Digital Operations & Industry 4.0
Automation, real-time monitoring, and smart analytics are reshaping operations strategy. Digital tools enable predictive maintenance, faster decision-making, and greater visibility across company operations, increasing the relevance in a data-driven economy.
Data-Driven Decision Making & KPIs
Modern operations management relies on performance dashboards and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure efficiency, quality, and delivery. These insights allow leaders to take proactive action rather than react to problems after they occur.
Together, these tools empower organizations to continuously strengthen their business operations, ensuring that improvement becomes a permanent part of how they operate—not just a temporary initiative.
Role of Operations Management in Business Growth & Competitiveness
Strong operations management is one of the most powerful drivers of sustainable business growth. When company operations are well structured, organizations can scale efficiently without losing control over cost, quality, or delivery. Effective management ensures that as volumes increase, business and operations remain aligned, preventing chaos and inefficiencies.

A well-executed management system also builds customer trust. Consistent quality, on-time delivery, and reliable service—across both service and manufacturing operations—strengthen brand reputation and encourage long-term customer loyalty. This highlights the true importance of operations management in creating dependable customer experiences.
From a strategic perspective, a strong strategy enables organizations to compete globally. Companies with optimized workflows, data-driven planning, and disciplined execution can respond faster to market changes, overcome challenges, and outperform less agile competitors. The functions of operations management such as capacity planning, quality control, and supply chain coordination form the backbone of this competitive advantage.
The growing relevance of operations management is also evident in its impact on profitability and resilience. By achieving the objectives—cost efficiency, flexibility, and reliability—organizations can protect margins even during economic uncertainty. In this way, strong operations are not just a support function but a strategic foundation for long-term success.
Why Businesses Need Expert Operations Management Consulting
Many organizations struggle to achieve strong operations management because internal teams are often focused on daily firefighting rather than long-term improvement. As company operations become more complex, the need for specialized expertise becomes critical.
Limited Internal Capabilities
Most internal teams lack advanced skills in processes management, data analytics, and performance benchmarking. This limits the effectiveness of operations and prevents organizations from achieving the full objectives such as cost efficiency and consistent quality.
Lack of Strategic Perspective
Without external insight, business and operations often become disconnected. Consultants bring a fresh, unbiased view that helps define a clear strategy aligned with market demands, reinforcing the importance of operations management in driving growth.
Unstructured Improvement Efforts
Many companies attempt to solve challenges without a structured approach. Expert consultants use proven frameworks to strengthen the functions of operations management, ensuring improvements are systematic and measurable.
Need for Faster, Sustainable Results
The growing relevance of operations management means organizations cannot afford slow or trial-and-error improvements. With benchmarking, best practices, and disciplined execution, consulting support delivers faster and more reliable performance improvements across all company operations.
FAQs
A. It is the discipline that plans, controls, and improves how company operations convert inputs into valuable products and services. The importance of it lies in its ability to reduce costs, improve quality, and align business and operations with customer expectations and long-term goals.
A. Strong processes management ensures that every activity in business follows a structured and efficient flow. By standardizing and improving workflows, organizations reduce errors, improve productivity, and strengthen their strategy across both manufacturing and services operations.
A. The main objectives include cost efficiency, quality consistency, fast delivery, flexibility, and sustainability. These objectives help organizations optimize their operations while supporting long-term business growth.
A. Typical challenges include poor process visibility, high operating costs, bottlenecks, inconsistent quality, and lack of data-driven decisions. These issues directly affect company operations and the overall effectiveness of operations management.
A. A strong operations strategy aligns business with market demand and competitive positioning. It enables organizations to scale, control costs, and deliver consistent quality across manufacturing and services operations.
A. The growing relevance is driven by rising customer expectations, global competition, and digital transformation. Businesses need strong processes management and analytics to remain competitive and resilient.
A. Effective business operations management reduces waste, improves productivity, and ensures consistent delivery. This supports the objectives and directly boosts profitability and customer satisfaction.
A.Investing in operations management helps organizations overcome challenges, strengthen their strategy, and turn company operations into a long-term competitive advantage.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive and unpredictable business landscape, operations management has emerged as a true strategic differentiator. Organizations that actively invest in strengthening their operations are better equipped to control costs, improve quality, and deliver consistent value to customers. The importance lies not only in efficiency, but in its ability to align business and operations toward long-term growth and sustainability.
Modern enterprises must move beyond reactive firefighting and adopt a forward-looking strategy. By applying structured processes management and strengthening the functions, companies can overcome persistent challenges such as inefficiencies, variability, and rising costs. This shift is critical, where customer expectations and competitive pressure continue to rise.
The growing relevance of operations management is also reflected in its direct impact on profitability, scalability, and resilience. When organizations focus on the objectives—cost control, quality excellence, speed, and flexibility—they transform business operations management into a powerful growth engine. Companies that treat operations as a strategic capability, rather than a support function, build the foundation for long-term success, stronger customer trust, and sustainable competitive advantage.
For more information, go to our Homepage.

