Work Measurement: A Critical Tool for Business Efficiency and Productivity
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, work measurement has become an essential practice
for organizations striving to achieve greater efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. Work measurement refers to the systematic determination of the time required for a qualified worker to complete a specified task according to a defined standard of performance. By establishing accurate time standards, companies can effectively manage resources, streamline operations, and eliminate bottlenecks.
The importance of measuring work cannot be overstated, especially in today’s competitive business environment. Accurate and scientific work measurement enables organizations to set realistic benchmarks, assess workforce productivity, and identify areas that need improvement. In fact, work measurement in operations management plays a pivotal role in process optimization, cost control, and continuous improvement initiatives. Through precise work measurement in operations management, businesses can ensure optimal utilization of both human and material resources, leading to higher output and reduced operational costs.
Moreover, work measurement in industrial engineering is a fundamental tool for designing efficient work systems and layouts. It aids in the evaluation of existing methods, the development of new processes, and the implementation of best practices across different departments. As industries across the globe embrace automation and advanced technologies, the role of work measurement in industrial engineering continues to expand, enabling organizations to achieve strategic goals and maintain a competitive edge.
In summary, the adoption of effective work measurement practices is crucial for businesses operating in today’s dynamic marketplace. By leveraging work measurement in operations management and in industrial engineering, companies can unlock higher productivity, minimize waste, and ensure sustainable growth.

What is Work Measurement?
Work measurement is a scientific and systematic process that determines the time needed for a qualified worker to accomplish a specific task under predefined conditions and to a set performance standard. At its core, work measurement focuses on identifying and analyzing each element of a job, ensuring that tasks are both efficient and realistic to achieve in the allotted time.
Key Elements of Work Measurement
- Systematic Determination of Time: The essential concept behind work measurement is to break down tasks into smaller, manageable elements and measure the time taken to complete each. By doing so, businesses gain accurate data about how long it should take to finish an assignment, leading to fair and reasonable standards.
- Differentiating Effective and Ineffective Time: Through careful observation and data collection, work measurement procedures help distinguish between effective time—when an employee is actively adding value—and ineffective time, which can arise from delays, interruptions, or unnecessary motions. This differentiation is crucial to identifying waste and improving productivity.
- Standardizing Processes: One of the main objectives of work measurement is to standardize work processes across the organization. By applying various methods of work measurement, companies ensure consistency, reduce variations, and make workloads more predictable. This not only improves quality but also provides a solid basis for evaluating and comparing employee performance.
Role in Performance and Benchmarking
Work measurement is indispensable when it comes to setting performance benchmarks and fair standards. By using proven work measurement procedures, organizations can:
- Establish clear expectations for task completion.
- Develop incentive systems and pay structures based on objective data.
- Benchmark progress and make informed decisions on process improvements.
- Ensure equitable distribution of tasks among employees.
In summary, the objectives of work measurement include increasing operational efficiency, reducing waste, and enabling data-driven management. Whether through direct observation, analytical techniques, or statistical sampling, the methods of work measurement provide a framework for ongoing improvement and optimization within every aspect of business operations.
Objectives of Work Measurement
The objectives of work measurement serve as the foundation for improving productivity and competitiveness in any organization. Through the systematic application of various methods of work measurement, businesses can gain invaluable insights into their operations and take actionable steps toward optimization.
Work measurement is not just about tracking time—it is about transforming the way tasks are performed and managed. The primary objectives of work measurement include:
Eliminating Wasted and Ineffective Time:
One of the fundamental objectives of work measurement is to identify and eliminate all forms of waste and ineffective time in business operations. By carefully applying the right work measurement procedure, organizations can pinpoint where delays, bottlenecks, or redundancies exist and take targeted actions to eradicate them. This leads directly to smoother workflows and higher productivity.
Establishing Standard Times for Tasks:
An important goal of work measurement is to set accurate and realistic standard times for various tasks. These standards empower companies to execute effective scheduling and workforce planning, ensuring that resources are optimally utilized and commitments are fulfilled consistently.
Improving Operational Efficiency and Reducing Labor Costs:
Efficient work measurement procedures reveal opportunities to streamline processes, which directly translates to lower labor costs and improved operational efficiency. By using the right methods of work measurement, organizations can redesign work to make the best use of both human and material resources.
Evaluating Worker Performance and Skill Levels:
Objective performance assessment is another key benefit. With well-established work measurement systems, management can fairly evaluate each worker’s output relative to predefined standards, helping identify training needs or skill gaps and providing a basis for recognizing outstanding performance.
Supporting Cost Control and Continuous Improvement:
Effective work measurement is a building block for cost control. By understanding how long each task should actually take, companies can better forecast costs, control budgets, and identify areas ripe for process improvements. The continuous review and refinement supported by work measurement procedures also enhance long-term competitiveness.
In conclusion, the objectives of work measurement are deeply interwoven with the pursuit of higher productivity, waste elimination, and cost efficiency. When the proper methods of work measurement and work measurement procedures are implemented, businesses can achieve measurable improvements in every aspect of their operations.
Techniques Used in Work Measurement
Understanding and applying the right methods of work measurement is essential for any organization aiming to optimize productivity and resources. A variety of work measurement techniques have been developed to suit different operational needs, each offering unique advantages in analyzing and improving work methods. Here’s an overview of the most widely used work measurement methods, with each technique designed to handle specific types of tasks and scenarios.
Time Study
This classic approach stands at the core of many work measurement methods. The process involves the direct observation and precise recording of the time required to complete each element of a job. As a foundational aspect of time study in work measurement, a trained observer typically uses a stopwatch or modern software tools to document the performance. This method is especially valuable for repetitive tasks, offering highly accurate, real-world data. Explore the details in our dedicated blog on Time Study
Predetermined Motion Time Systems (PMTS)
Among the more advanced work measurement techniques, PMTS assigns standard time values to basic human motions. These systems—such as MTM (Methods-Time Measurement) or MOST (Maynard Operation Sequence Technique)—enable analysts to estimate task durations even before actual production begins. As a distinct type of work measurement, PMTS is commonly used for detailed process planning and automation design. For a comprehensive guide, visit our blog on Predetermined Motion Time Systems (PMTS)
Work Sampling
This work measurement technique uses statistical sampling to estimate the proportion of time workers spend on various activities. Rather than continuous observation, analysts record activities at randomly selected intervals. Work sampling is ideal for less repetitive or more varied tasks, and is considered one of the most efficient work measurement methods for large-scale operations. Learn more in our post on Work Sampling
Analytical Estimating
For complex, unique, or non-repetitive jobs—where standard times aren’t available—analytical estimating becomes invaluable. Using expert judgment and historical data, estimators break down a task, predict the time each component will require, and sum these to arrive at a total. This approach broadens the arsenal of types of work measurement, allowing flexibility across diverse industrial settings.
Synthesis from Elemental Data
In this approach, analysts combine established time values for job elements previously measured by other work measurement techniques. This method is efficient for tasks composed of commonly repeated elements, saving time on fresh observations and leveraging existing data within the organization.
Standard Data Systems
Leveraging historical records, standard data systems provide ready-to-use time values for repetitive operations. These systems represent both a category and practical tool among the methods of work measurement, supporting rapid analysis and standardization across multiple business units.
Applying multiple types of work measurement ensures more accuracy and adaptability in process analysis. Each of these work measurement techniques—from traditional time study in work measurement to innovative PMTS—offers unique insights and supports a culture of continuous improvement, enhancing both operational efficiency and competitiveness.
By integrating a variety of work measurement methods, organizations can tailor their approach to specific workflows, optimize performance monitoring, and drive significant improvements in productivity and cost control.
Standard Time and Its Calculation
Standard time calculation forms the backbone of workforce optimization and operational efficiency in any modern industry. Understanding how to calculate standard time ensures fair evaluation, better planning, and sustainable process improvements.
Standard time refers to the total amount of time a qualified worker should take to complete one unit of a task, working at a defined level of performance and under normal conditions. Mastery over the process of standard time calculation allows businesses to set benchmarks, budget labor, and assess productivity systematically.
Why is Standard Time Important?
A robust standard time calculation empowers organizations to:
- Plan workforce requirements accurately.
- Establish realistic schedules and deadlines.
- Set performance standards and incentive schemes.
- Control labor costs and improve efficiency.
- Identify process improvements proactively.
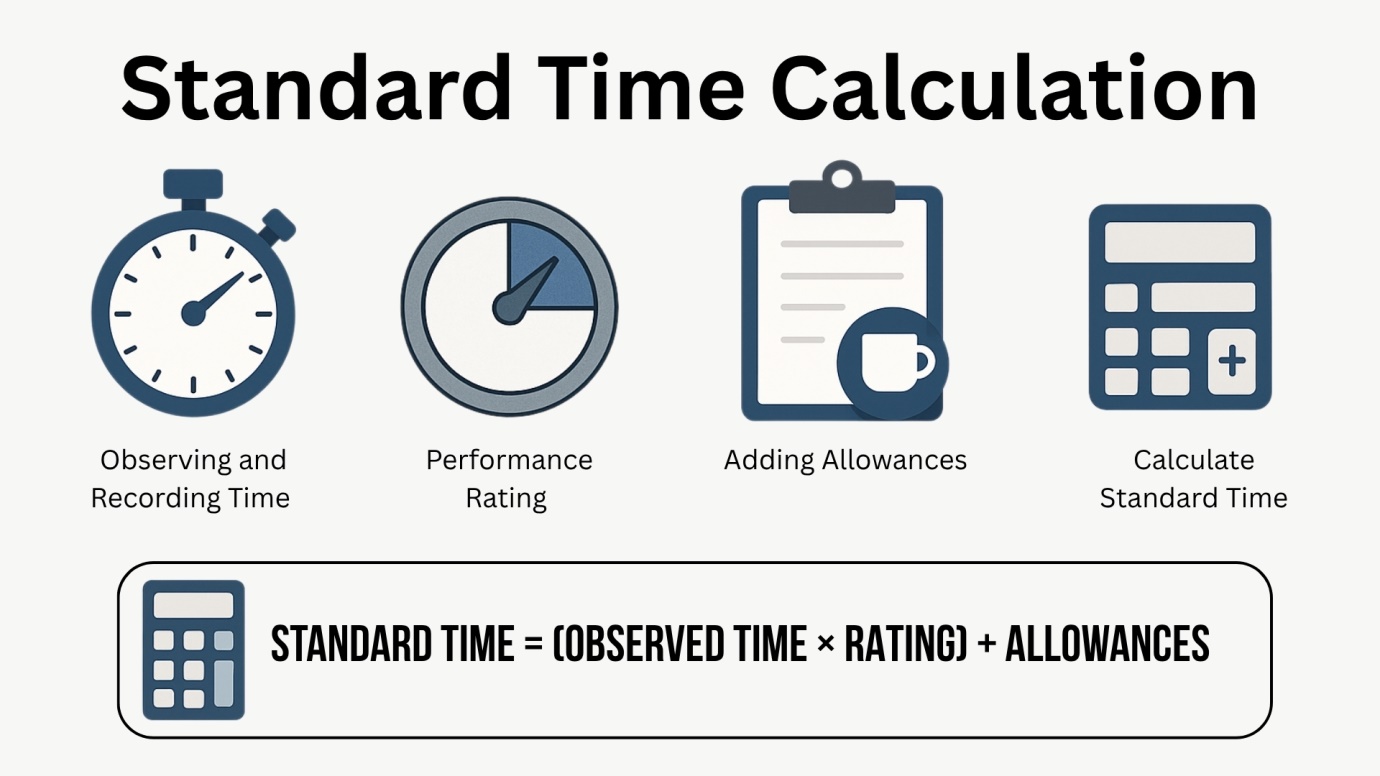
How to Calculate Standard Time
The process of how to calculate standard time is a blend of observation, scientific analysis, and practical adjustments to account for real-world variables. Here’s an easy-to-follow breakdown:
1. Observing and Recording Time for Task Elements
- Carefully observe each element or step involved in the job.
- Record the actual time taken to complete each element (the observed time).
2. Applying Performance Rating Factors
- Evaluate the worker’s pace in relation to the defined standard performance.
- Multiply the observed time by the performance rating to convert to “normal” time.
3. Adding Allowances
- Factor in necessary allowances for fatigue, unavoidable delays, and other contingencies.
- Ensure the standard time calculation is realistic and accounts for practical interruptions.
Formula:
Standard Time = (Observed Time × Rating) + Allowances
By prioritizing accurate standard time calculation, organizations can reinforce fairness, maximize productivity, and create a culture of continuous improvement—all vital for long-term efficiency and competitiveness.
The Work Measurement Process
Implementing an effective work measurement process is essential for any organization seeking to enhance productivity, streamline operations, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. The process of work measurement involves a series of methodical steps that guide businesses from recognizing the need for measurement to establishing and using reliable time standards. By following structured work measurement techniques and utilizing varied methods of work measurement, organizations can ensure consistent, accurate, and actionable results.
Here’s a breakdown of a proven work measurement process:
Defining Objectives and Scope
The first step in the work measurement process is clearly defining the objectives and the scope of the task under study. Whether your goal is to boost productivity, reduce waste, or improve resource allocation, it’s crucial to identify what outcomes you expect from the work measurement and what processes or activities will be included.
Choosing the Appropriate Technique
Selecting the right work measurement techniques is vital. The selection depends on the nature and complexity of the task. For repetitive jobs, direct time study (a classic method of work measurement) might be best. For tasks with more variability, work sampling or analytical estimating are recommended methods of work measurement. The correct choice ensures the process is efficient and results are meaningful.
Collecting Data Efficiently
Accurate data collection is at the heart of work measurement. This stage often involves tools such as stopwatches for manual observation, advanced software for automatic tracking, and detailed process charts. Thorough and unbiased observation during this phase is critical to capturing the real picture of how work is performed, forming the foundation for subsequent analysis using selected work measurement techniques.
Analyzing Data, Applying Rating Factors, and Calculating Allowances
Once the data has been gathered, it must be analyzed to determine the “normal” time for each task. This includes applying appropriate rating factors to account for variations in worker performance and adding allowances for fatigue, rest breaks, and unavoidable delays. These analytical steps ensure that results generated from the selected methods of work measurement are both fair and practical.
Setting Standard Times and Integrating Improvements
The final stage is to set standard times for each task based on your analysis, using the most effective work measurement techniques. Once established, these time standards can be integrated into daily workflows, supporting better scheduling, resource planning, training, and performance review. This integration is also where organizations can spot opportunities for process improvement and implement best practices, driving operational excellence.
By meticulously following the systematic work measurement process and leveraging diverse methods of work measurement, companies can create a robust operational framework that leads to ongoing performance improvement, higher efficiency, and a distinct competitive edge.
Benefits of Implementing Work Measurement
Utilizing work measurement in your organization can transform productivity and drive operational success. By leveraging proven methods of work measurement and advanced work measurement techniques, companies can unlock a multitude of advantages that enhance performance across the board.
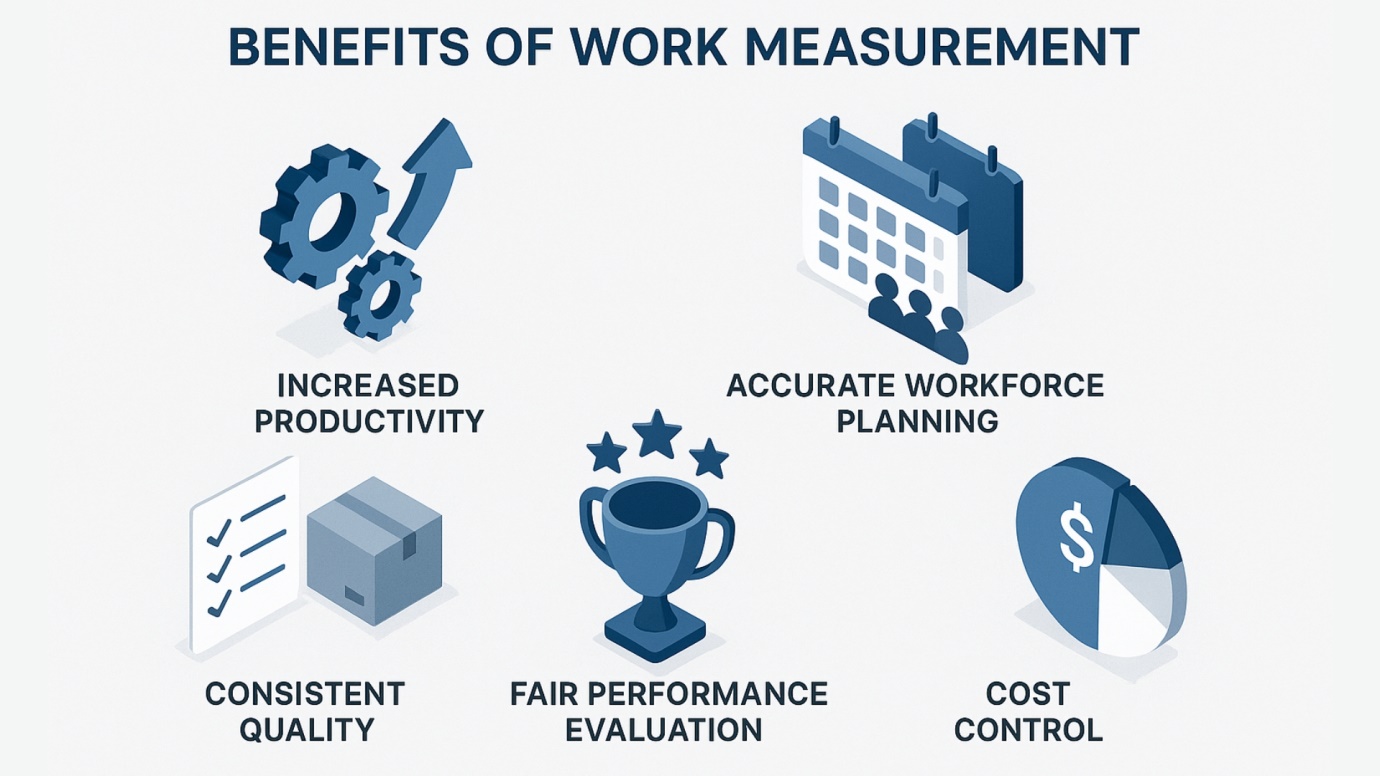
Key Benefits of Work Measurement:
Enhanced Productivity Through Elimination of Inefficiencies
One of the primary benefits of work measurement is the ability to systematically identify and eliminate inefficiencies in workflows. Using precise work measurement techniques, businesses can pinpoint bottlenecks, reduce repetitive motions, and streamline tasks. This leads to smoother operations where every team member’s efforts are maximized.
Accurate Workforce Planning and Better Resource Allocation
Through scientific methods of work measurement, managers gain clear insight into how long it should take to complete specific tasks. This allows for more accurate workforce planning—ensuring the right number of employees are assigned to the right jobs at the right times. Effective work measurement helps organizations allocate resources precisely where they are needed, reducing both overstaffing and understaffing.
Improved Quality and Consistency of Output
Implementing standardized work measurement procedures enables companies to maintain consistent production rates and product quality. When everyone works to the same standards, quality variations are minimized and consistency becomes the norm. This is only possible when the most suitable work measurement techniques are integrated into daily operations.
Realistic Performance Evaluations and Incentive Systems
With accurate benchmarks set via reliable work measurement, performance evaluations become fair and objective. Employees know what is expected of them and can be rewarded for exceeding standards. This transparency boosts morale and enables management to create effective incentive systems that drive higher achievement.
Effective Cost Management and Competitive Pricing
By employing the right methods of work measurement, organizations achieve better control over labor costs and operational budgets. Knowing the time and resources needed for each activity empowers managers to price products and services competitively. This cost transparency supports profitability and positions companies advantageously in the marketplace.
Implementing work measurement is a strategic investment in sustained excellence. The benefits extend beyond productivity gains: organizations experience stronger teamwork, adaptability to change, and long-term stability. With a robust system built on modern work measurement techniques and rigorous methods of work measurement, any business can elevate its operational performance and stay ahead in today’s competitive environment.
FAQs
A. Work measurement is the systematic process of determining the time a qualified worker takes to complete a task at a defined performance level. It is important because it helps businesses optimize productivity, eliminate inefficiencies, and set realistic performance standards using proven work measurement techniques.
A. The objectives of work measurement include eliminating wasted time, establishing standard times, improving operational efficiency, evaluating worker performance, and supporting cost control efforts. These goals help organizations enhance productivity and resource planning.
A. Common methods of work measurement include direct time studies, predetermined motion time systems (PMTS), work sampling, analytical estimating, synthesis from elemental data, and the use of standard data systems. Each method is suited to different types of tasks and operational needs.
A. Time study in work measurement involves observing and recording the time taken to complete each element of a task using tools like stopwatches. The data collected supports standard time calculation and sets benchmarks for performance.
A. The standard work measurement procedure involves defining objectives, selecting suitable measurement techniques, collecting time data, applying rating factors, calculating allowances, and finally setting standard times for tasks. This structured approach ensures fair and accurate standards.
A. Standard time calculation is performed by multiplying the observed time for a task by a performance rating and then adding allowances for fatigue, delays, and contingencies. This results in a realistic time standard that matches working conditions.
A. Yes, work measurement provides precise data on how long tasks should take, enabling managers to plan workforce requirements more effectively and allocate resources optimally for better productivity.
A. For non-repetitive or complex tasks, analytical estimating and synthesis from elemental data are often the most suitable work measurement techniques where direct time study may not be practical.
A. PMTS assign standard time values to basic human motions, allowing for quick task duration estimation without the need for direct observation. This is an advanced work measurement method especially useful in process design and automation.
A. Work measurement in industrial engineering focuses on analyzing and optimizing the time and methods used to perform tasks. It helps industrial engineers design efficient systems, improve workflows, reduce wasted time, and enhance overall productivity. For a deeper understanding, visit our industrial engineering page.
A. Typical tools in the work measurement procedure include stopwatches, data collection software, video recordings, and observational checklists for capturing accurate timing and performance data.
Conclusion
In today’s highly competitive and dynamic marketplace, the implementation of effective work measurement stands as a cornerstone for operational excellence and sustainable business growth. By embracing reliable methods of work measurement and establishing a robust work measurement procedure, organizations gain the critical insights needed to optimize every facet of their operations.

Work measurement plays an indispensable role in modern business operations by:
- Setting objective standards and clear expectations for every task.
- Driving efficiency by identifying and eliminating hidden inefficiencies.
- Enabling fair and transparent performance evaluations.
- Supporting strategic decision-making through accurate data and analytics.
When companies adopt proven methods of work measurement and invest in a comprehensive work measurement procedure, they position themselves to manage labor costs effectively, improve resource allocation, and boost productivity across all departments.
Work measurement is not only about tracking time—it’s about transforming business processes and cultivating a culture of continuous improvement. By incorporating advanced work measurement techniques into daily workflows, businesses can ensure consistency, improve quality, and maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
The path to operational excellence and consistent growth begins with a commitment to work measurement. We encourage every forward-thinking organization to evaluate and enhance their current practices by adopting modern methods of work measurement and refining their work measurement procedure. Doing so will not only lead to higher levels of efficiency but also foster long-term sustainability and business success.
Let work measurement be the strategic advantage your business needs to excel today—and into the future.
To learn more about Sugoya India and our expert consultation services, visit our Homepage.

